The Elasticity and Incentives Project Graph emerges as a powerful tool in project management, combining economic principles and visual representation to enhance analysis and motivation. This concept provides a comprehensive framework for understanding consumer behavior and project progress, enabling businesses and organizations to optimize their strategies and achieve exceptional outcomes.
Delving into the intricacies of elasticity, we explore its various types and applications in analyzing consumer behavior. The project graph, a visual representation of project progress, serves as a valuable tool for tracking milestones and identifying potential challenges.
Elasticity and Incentives
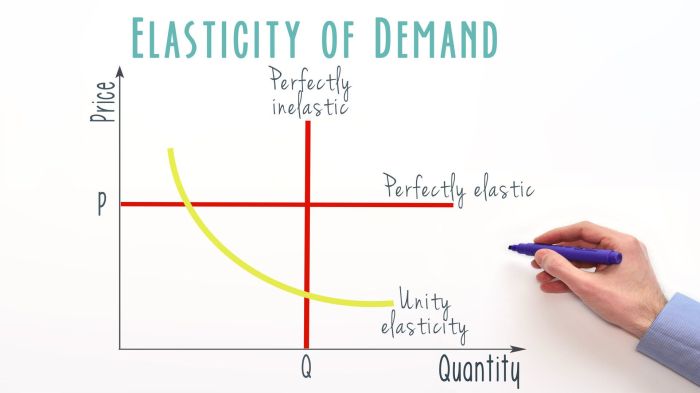
In economics, elasticity measures the responsiveness of one economic variable to changes in another. It is a crucial concept for understanding consumer behavior and market dynamics.
Types of Elasticity
- Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price.
- Income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in income.
- Cross-price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded for one good to changes in the price of another good.
Examples of Elasticity in Consumer Behavior
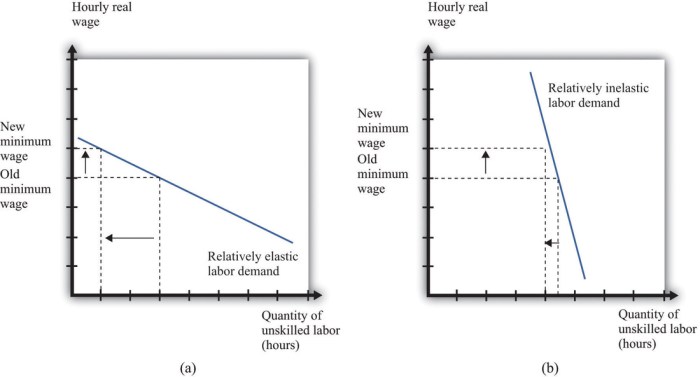
- If the price of a good increases and demand decreases significantly, the good is considered price elastic.
- If a consumer’s income increases and their demand for a luxury good increases proportionally, the good has a high income elasticity.
- If the price of a substitute good decreases and the demand for a complementary good increases, the goods have a positive cross-price elasticity.
Project Graph
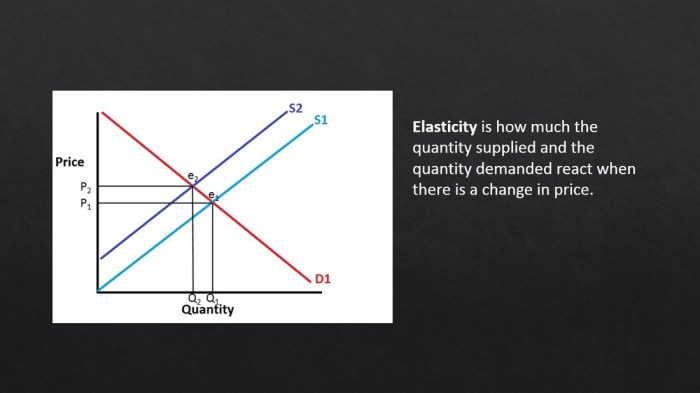
A project graph is a visual representation of the progress of a project. It tracks key milestones, tasks, and dependencies, providing a comprehensive overview of the project’s status.
Uses of Project Graphs
- Tracking the completion of tasks and deliverables.
- Identifying potential delays and bottlenecks.
- Monitoring the progress of multiple projects simultaneously.
Examples of Project Graphs in Different Industries
- Software development:Tracking the progress of software development sprints and releases.
- Construction:Monitoring the completion of construction phases and milestones.
- Marketing:Tracking the progress of marketing campaigns and initiatives.
Using Elasticity and Incentives to Analyze Project Graphs
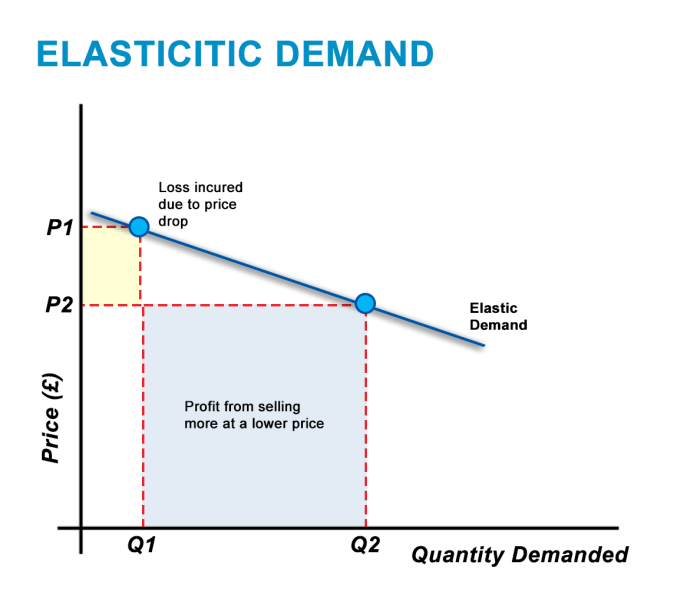
Elasticity and incentives can be powerful tools for analyzing and managing project graphs.
Elasticity in Project Graphs
Elasticity can be used to measure the responsiveness of project tasks to changes in resources, timelines, or incentives. For example, if a project task is highly elastic with respect to resources, adding more resources will significantly reduce the task’s completion time.
Incentives in Project Graphs
Incentives can be used to motivate team members to complete tasks on time or to exceed expectations. For example, offering bonuses or rewards for completing tasks ahead of schedule can increase the elasticity of project tasks with respect to timelines.
Examples of Using Elasticity and Incentives, Elasticity and incentives project graph
- A software development team may use elasticity to determine the optimal number of developers to assign to a project based on the project’s deadlines.
- A construction company may use incentives to motivate workers to complete a project ahead of schedule, reducing potential delays and penalties.
Top FAQs: Elasticity And Incentives Project Graph
What is elasticity in economics?
Elasticity measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded or supplied to changes in price or other factors.
How can elasticity be used to analyze consumer behavior?
Elasticity provides insights into how consumers adjust their consumption patterns in response to price changes and other market conditions.
What is the purpose of a project graph?
A project graph visually represents the progress of a project, allowing stakeholders to track milestones and identify potential delays or roadblocks.
How can incentives be used to motivate team members?
Incentives, such as bonuses or recognition, can encourage team members to perform better and contribute to the successful completion of a project.