Mutations worksheet part 1 gene mutations – As we embark on the Mutations Worksheet Part 1: Gene Mutations, let us delve into the intricate world of genetics, where gene mutations hold a pivotal role in shaping the tapestry of life. This comprehensive exploration will shed light on the nature, causes, and consequences of gene mutations, equipping us with a deeper understanding of their profound impact on our genetic makeup.
Through an engaging journey, we will uncover the mechanisms underlying gene mutations, their diverse types and effects, and the profound implications they hold for our health and development. Join us as we unravel the complexities of gene mutations, gaining valuable insights that will illuminate this fascinating realm of genetics.
Definition of Gene Mutations
Gene mutations are alterations in the DNA sequence of a gene, resulting in changes to the structure or function of the protein encoded by that gene. Mutations can be spontaneous or induced by environmental factors, and they play a crucial role in genetic diversity and evolution.
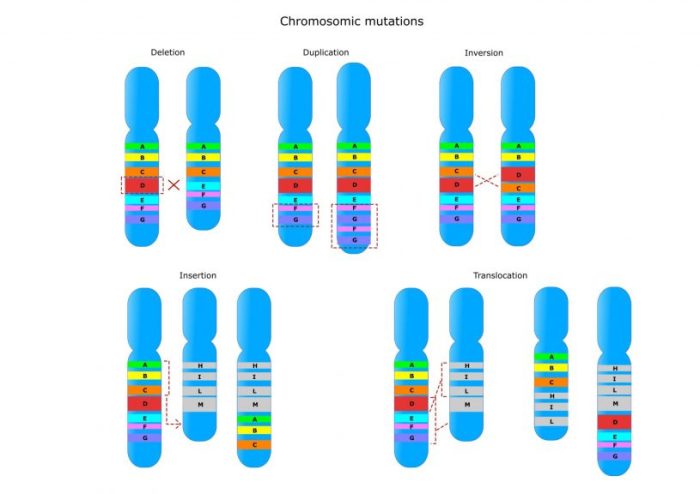
Types of gene mutations include:
- Point mutations:Single nucleotide changes that can result in missense, nonsense, or silent mutations.
- Insertions and deletions:Addition or removal of nucleotides, which can cause frameshifts and alter the reading frame of the gene.
- Duplications:Replication errors that result in multiple copies of a particular DNA sequence.
- Inversions:Reversal of the orientation of a DNA segment.
- Translocations:Exchange of genetic material between different chromosomes.
Causes of Gene Mutations: Mutations Worksheet Part 1 Gene Mutations
Gene mutations can be caused by various factors, including:
- Environmental factors:Radiation, chemicals, and certain viruses can damage DNA and induce mutations.
- DNA replication errors:Mistakes during DNA replication can lead to point mutations, insertions, or deletions.
- Transposable elements:Mobile genetic elements can insert themselves into genes, causing mutations.
- Oxidative stress:Reactive oxygen species can damage DNA and contribute to mutations.
Types of Gene Mutations
| Type | Characteristics | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Point mutations | Single nucleotide changes | Missense: Changes amino acidNonsense: Introduces a stop codonSilent: No effect on protein |
| Insertions and deletions | Addition or removal of nucleotides | Frameshifts: Alter reading frame, often causing truncated proteinsIn-frame: May have little or no effect |
| Duplications | Multiple copies of a DNA sequence | Increased gene dosage, which can lead to genetic disorders |
| Inversions | Reversal of DNA segment orientation | May disrupt gene expression or cause chromosomal rearrangements |
| Translocations | Exchange of genetic material between chromosomes | Can disrupt gene expression, cause chromosomal imbalances, or lead to cancer |
Consequences of Gene Mutations
Gene mutations can have a wide range of consequences, including:
- Loss of function:Mutations that disrupt gene function can lead to genetic diseases.
- Gain of function:Mutations that activate or enhance gene function can also cause genetic disorders.
- Dominant mutations:Mutations that occur in one copy of a gene can be sufficient to cause a genetic disorder.
- Recessive mutations:Mutations that occur in both copies of a gene are necessary to cause a genetic disorder.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of gene mutations in genetics?
Gene mutations play a crucial role in genetics as they introduce variations into the genetic code, potentially leading to new traits and adaptations. These mutations can be spontaneous or induced by environmental factors, and their effects can range from beneficial to detrimental.
How do gene mutations contribute to genetic disorders?
Gene mutations can disrupt the normal function of genes, leading to genetic disorders. These disorders can manifest in various ways, depending on the type of mutation and the gene affected. Some common genetic disorders include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington’s disease.
What are the ethical implications of gene mutation research?
Gene mutation research raises ethical concerns related to the potential misuse of genetic information and the unintended consequences of manipulating the human genome. It is essential to consider the potential benefits and risks associated with gene editing and genetic engineering, ensuring responsible and ethical practices.