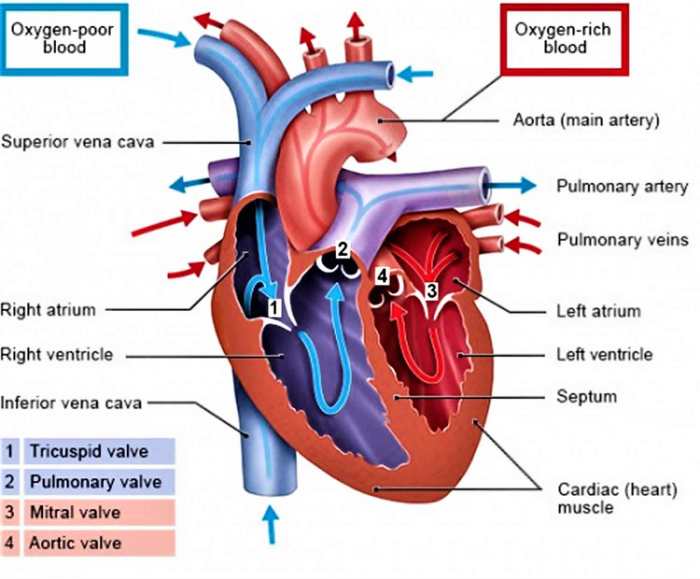
Match the following term with its correct description tricuspid valve – Delving into the intricacies of cardiology, we embark on an exploration of the tricuspid valve, a crucial component of the heart’s circulatory system. Its pivotal role in regulating blood flow warrants a comprehensive understanding, which we shall endeavor to provide in this discourse.
Nestled within the right atrium and ventricle, the tricuspid valve orchestrates the unidirectional flow of blood from the atrium to the ventricle. Its intricate structure, composed of three leaflets, chordae tendineae, and papillary muscles, ensures efficient valve function.
Introduction
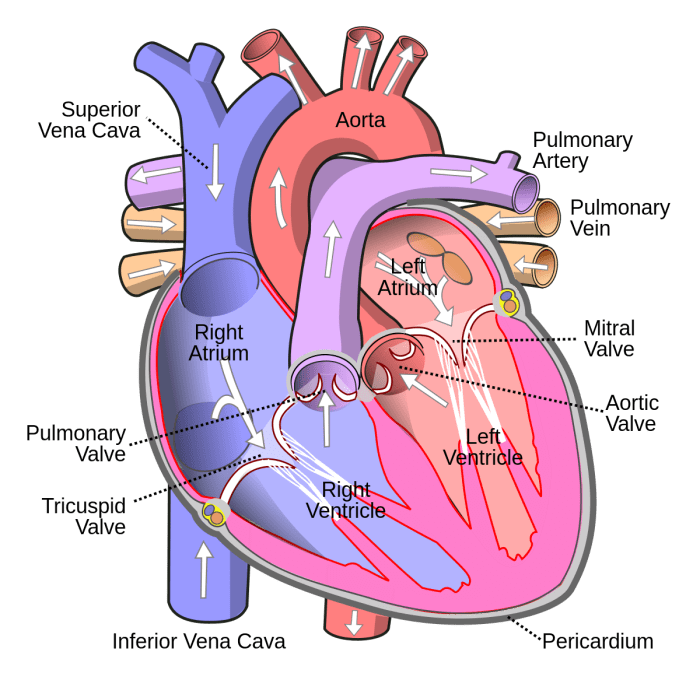
The tricuspid valve is a crucial component of the heart’s circulatory system, responsible for maintaining unidirectional blood flow between the right atrium and right ventricle. It is located at the atrioventricular junction and plays a vital role in preventing backflow of blood into the right atrium during ventricular systole.
Anatomy of the Tricuspid Valve: Match The Following Term With Its Correct Description Tricuspid Valve
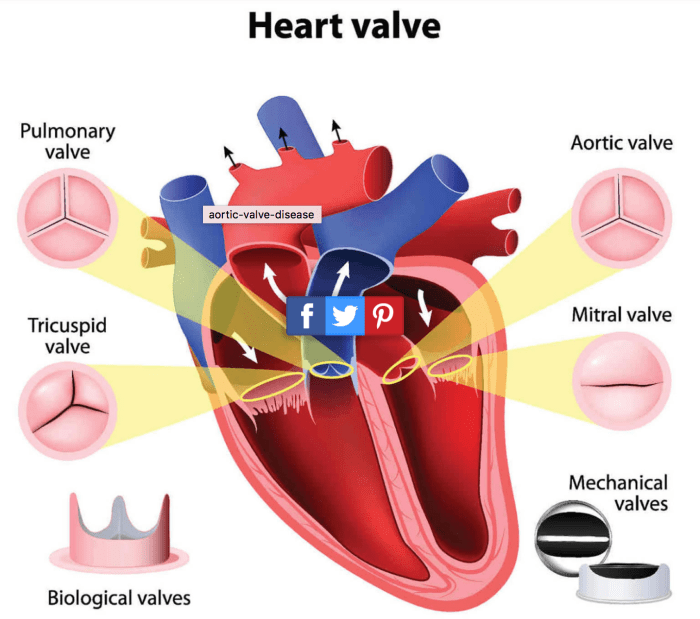
The tricuspid valve consists of three thin, cusp-like leaflets that are attached to the fibrous skeleton of the heart. These leaflets are supported by chordae tendineae, which are thin, fibrous cords that connect the leaflets to the papillary muscles of the right ventricle.
The papillary muscles contract during ventricular systole, pulling the chordae tendineae and closing the tricuspid valve.
Physiology of the Tricuspid Valve
The tricuspid valve opens passively during ventricular diastole when the pressure in the right ventricle falls below the pressure in the right atrium. This allows blood to flow from the right atrium into the right ventricle. During ventricular systole, the pressure in the right ventricle increases, causing the tricuspid valve to close and preventing backflow of blood into the right atrium.
Clinical Significance of Tricuspid Valve Disorders
Tricuspid valve disorders can be either regurgitation or stenosis. Regurgitation occurs when the tricuspid valve does not close properly, allowing blood to leak back into the right atrium. Stenosis occurs when the tricuspid valve is narrowed, obstructing blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
Both regurgitation and stenosis can lead to right-sided heart failure if left untreated.
Treatment Options for Tricuspid Valve Disorders, Match the following term with its correct description tricuspid valve
Treatment for tricuspid valve disorders depends on the severity of the condition. Medical therapy may be used to manage symptoms, such as diuretics to reduce fluid retention and vasodilators to lower blood pressure. Surgical intervention may be necessary to repair or replace the tricuspid valve.
Transcatheter procedures, such as balloon valvuloplasty or valve replacement, may also be used to treat tricuspid valve disorders.
Prevention of Tricuspid Valve Disorders
There are no specific measures to prevent tricuspid valve disorders, but managing underlying conditions that can damage the valve, such as rheumatic fever and infective endocarditis, can help reduce the risk of developing tricuspid valve disease.
Clarifying Questions
What is the primary function of the tricuspid valve?
The tricuspid valve prevents the backflow of blood from the right ventricle to the right atrium during ventricular contraction.
What are the common types of tricuspid valve disorders?
Tricuspid valve regurgitation (leakage) and tricuspid valve stenosis (narrowing) are the most prevalent types of tricuspid valve disorders.
How is tricuspid valve regurgitation diagnosed?
Echocardiography, a non-invasive imaging technique, is commonly used to diagnose tricuspid valve regurgitation by visualizing the valve and assessing blood flow patterns.